The Evolution of Tractors: From Horse-Drawn to Modern Machines
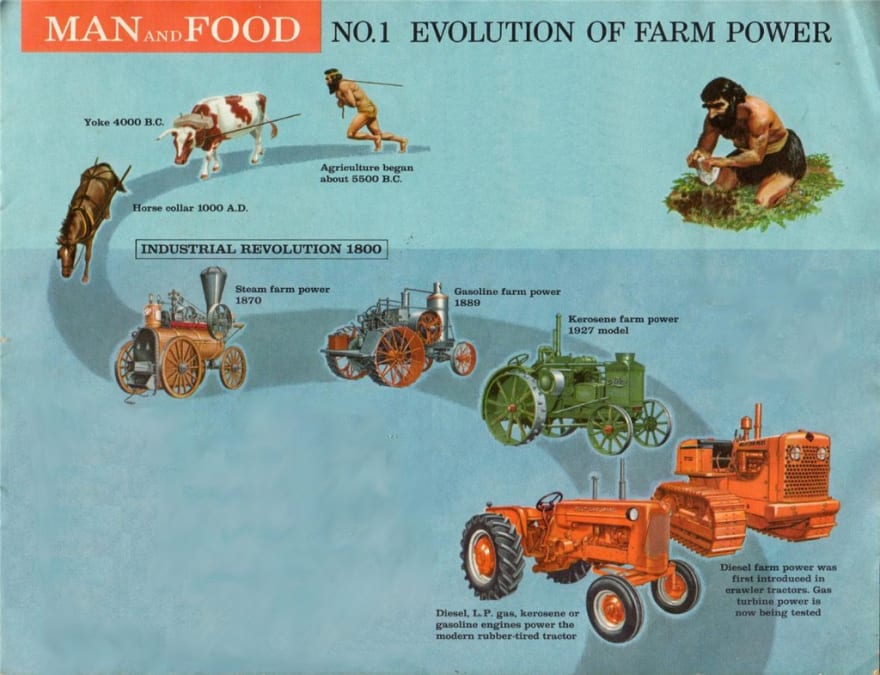
The tractor has completely changed how we manage farms, develop land, and harvest crops. It is an essential instrument in modern agriculture. Tractors are not always the effective, complex vehicles we are comfortable with. It’s an amazing story of creation and improvement from horse-drawn plows to the twenty-first century’s advanced, controlled computer tractors. Exploring the history of tractors from the first days of mechanized farming to the cutting-edge technology influencing agriculture in the future, this article examines the evolution of tractors.
The Age of Horse-Drawn Plows: Early Agricultural Practices

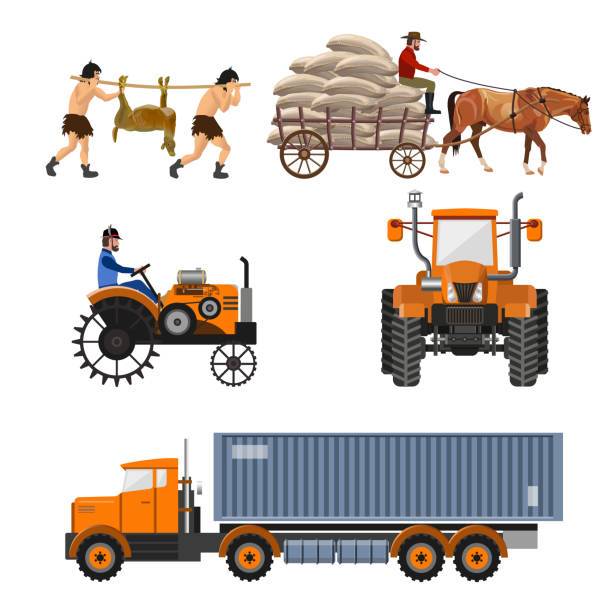
Farming required a lot of labor and depended primarily on human and animal power before tractors were invented. In the past, the horse-drawn plow was the main implement for cultivating the ground. Using the power of their feet, farmers would plow the land using horses, cattle, or donkeys. Despite its effectiveness, this method was labor-intensive and slow, which limited the size of farming operations.
Key Characteristics:
- Depended on animal labor.
- Limited to small-scale farming.
- Required significant physical effort from farmers.
The Evolution of the Steam-Powered Tractors: 19th Century Innovations
The invention of machinery powered by steam was one of the significant developments regarding farming brought about by the Industrial Age. The earliest steam-powered tractors appeared in the middle of the 19th century; they were also referred to as steam plows or steam engines. These were large, heavy machinery that frequently needed many men to operate. Large fields were ploughed and enormous loads were hauled with them.
Key Characteristics:
- Steam engines are powered by coal or wood.
- Large and heavy, with limited maneuverability.
- Primarily used for plowing and transportation.
While steam tractors were a significant advancement, they had their limitations. They were expensive to produce and operate, and their size made them impractical for many farms. Nevertheless, they marked the beginning of mechanized farming, paving the way for more efficient agricultural practices.
The Introduction of Gasoline-Powered Tractors: Early 20th Century
Tractor innovation advanced significantly in the first half of the twentieth century with the introduction of fuel-injected machines. These engines were more efficient, more portable, and easier to operate than their steam-powered equivalents. In 1917, Henry Ford debuted the Fordson Model F, the first tractor with fuel injection to find popularity. It was inexpensive, mass-produced, and quickly became popular among farmers.
Key Characteristics:
- Powered by gasoline engines.
- Smaller, lighter, and more maneuverable than steam tractors.
- Mass production made them affordable for many farmers.
The success of the Fordson Model F and other early gasoline tractors revolutionized farming, allowing farmers to work larger fields with less effort. This period marked the beginning of the widespread adoption of tractors in agriculture.
The Rise of Diesel Tractors: Mid-20th Century
As tractor innovation developed further, diesel engines were established as the standard option for farm equipment. Compared to petrol engines, diesel-powered engines have several advantages, such as higher torque, extended machine life, and better fuel economy. Although diesel-powered tractors initially made their appearance in the 1920s, they didn’t take over as the most common kind of tractor before the middle of the 20th century.
Key Characteristics:
- Powered by diesel engines, offering better fuel efficiency.
- More powerful, with greater torque for heavy-duty tasks.
- Became the standard in agricultural machinery.
Additionally improving farming’s efficiency and productivity was the wide use of diesel tractors, which could run longer hours, handle heavier implements, and execute a greater variety of activities, from planting and plowing to harvesting and carrying.
The Advent of Modern Tractors: Late 20th to Early 21st Century
The latter part of the 20th century saw an immediate development in tractor technology with the development of satellite navigation systems, digital controls, and advanced hydraulic systems. These innovations transformed tractors into extremely advanced machines that perform exact, robotic tasks. Variable rate technology (VRT), telematics systems, and auto-steering are just some of the innovations that are making it possible for current tractors to perform agricultural tasks with an unprecedented degree of efficiency and precision.
Key Characteristics:
- Equipped with computerized controls and GPS systems.
- Capable of automated operations, including auto-steering and precision planting.
- Advanced hydraulics and PTO systems for handling a wide range of implements.
Precision agriculture, in which farmers utilize automation and data to optimize every part of their operations, has become more popular as a result of the incorporation of technology into tractors. Higher agricultural yields, less waste, and more environmentally friendly farming methods are the outcomes of this.
The Future of Tractors: Autonomous and Electric Machines
Considering the future, autonomous and electric technology are expected to dominate the tractor market. In certain regions of the world, autonomous tractors—tractors that can run without the need for human intervention—are currently undergoing testing and deployment. These devices are capable of continuous operation and previously unthinkable levels of precision in their task performance.
Key Characteristics:
- Autonomous operation with minimal human input.
- Electric powertrains for reduced emissions and lower operating costs.
- Integration with farm management software for seamless operation.
A growing number of farmers are turning to electric tractors as environmentally friendly substitutes for diesel-powered equipment. These tractors are a desirable choice for farmers who care about the environment because they operate more quietly, emit fewer emissions, and have lower running expenses.
Also, read about Seed Spreader Tractors
Conclusion on the Evolution of Tractors
Tractors have evolved from being horse-drawn cultivators to skilled technical devices over the previous 200 years, illustrating the incredible advances in the agricultural industry. Tractors are going to grow even more essential to feeding the world’s population as it grows because they boost productivity in agriculture, sustainability, and efficiency. Hence tractors are expected to evolve and revolutionize in the future, whether or whether they electrify power or utilize autonomous technology.










